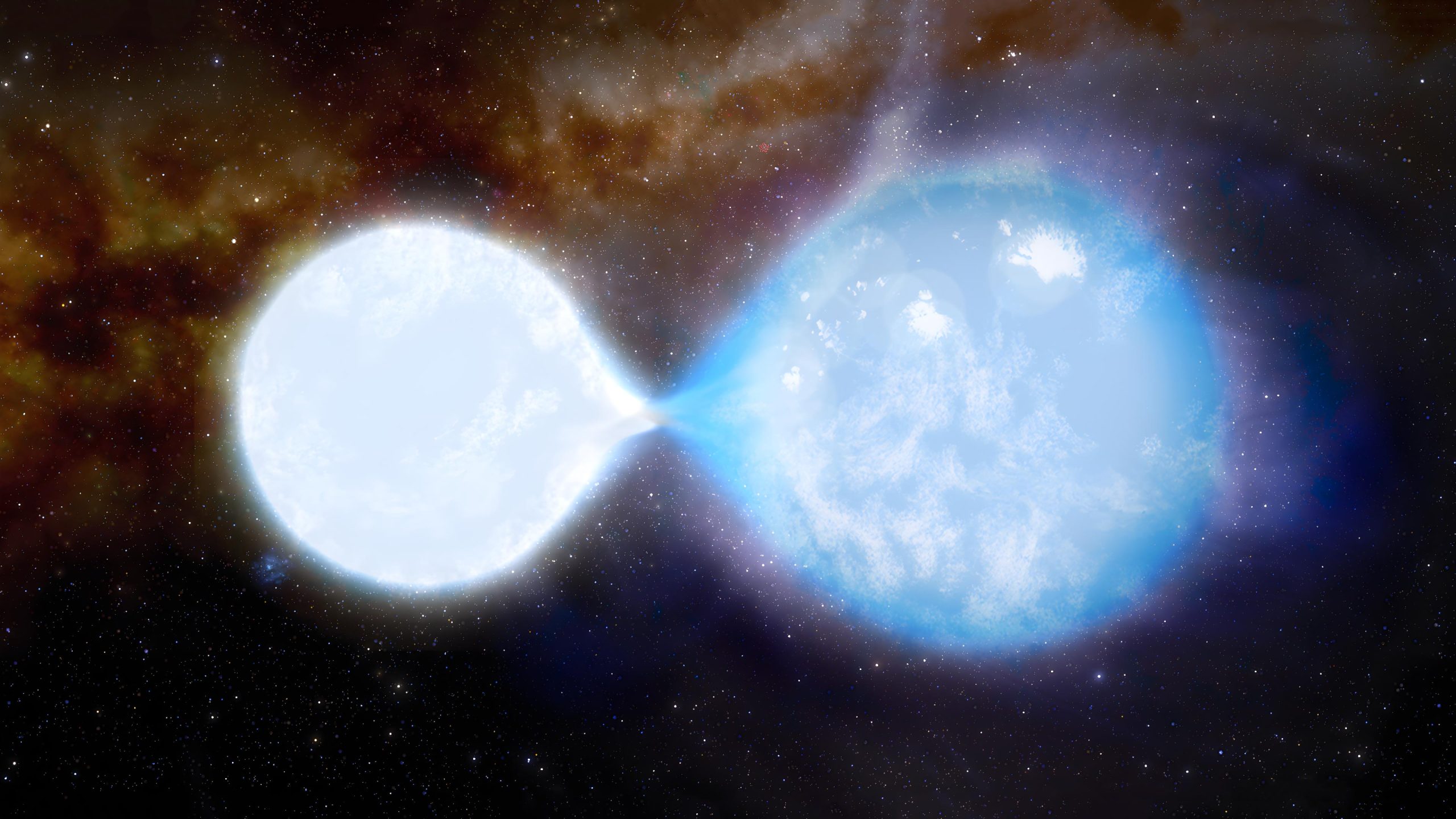
우리 태양 질량의 32배인 더 작고 더 밝고 더 뜨거운 별(왼쪽)은 현재 우리 태양 질량의 55배인 더 큰 동반자(오른쪽)에게 질량을 잃고 있습니다. 별들은 너무 뜨거워서 하얗고 파랗습니다. 각각 43,000도와 38,000도입니다. 신용: UCL/J.daSilva
유니버시티 칼리지 런던(University College London)과 포츠담 대학교(University of Potsdam) 연구원들의 새로운 연구에 따르면 이웃 은하에 있는 두 개의 거대한 접촉 별이 블랙홀이 되어 결국 함께 충돌하여 시공간 구조에 잔물결을 일으킬 것이라고 밝혔습니다.
이 연구는 저널에 게재되도록 승인되었습니다. 천문학 및 천체물리학알려진 쌍성(상호 무게 중심을 공전하는 두 개의 별)을 살펴보고 지상 기반 망원경과 우주 기반 망원경의 조합에서 얻은 별빛을 분석했습니다.
연구자들은 Small Magellanic Cloud라고 불리는 이웃한 왜소 은하에 위치한 별들이 서로 부분적으로 접촉하고 물질을 교환하고 있으며 현재 한 별이 다른 별을 먹고 있음을 발견했습니다. 그들은 3일마다 서로 궤도를 돌며 지금까지 관찰된 가장 큰 접촉 별(접촉 쌍성으로 알려짐)입니다.
관측 결과를 쌍성의 진화에 대한 이론적 모델과 비교한 결과, 가장 적합한 모델에서 현재 공급되고 있는 별이 블랙홀이 되어 동반자 별을 공급할 것이라는 사실을 발견했습니다. 남은 별은[{” attribute=””>black hole shortly after.
These black holes will form in only a couple of million years, but will then orbit each other for billions of years before colliding with such force that they will generate gravitational waves – ripples in the fabric of space-time – that could theoretically be detected with instruments on Earth.
PhD student Matthew Rickard (UCL Physics & Astronomy), lead author of the study, said: “Thanks to gravitational wave detectors Virgo and LIGO, dozens of black hole mergers have been detected in the last few years. But so far we have yet to observe stars that are predicted to collapse into black holes of this size and merge in a time scale shorter than or even broadly comparable to the age of the universe.
“Our best-fit model suggests these stars will merge as black holes in 18 billion years. Finding stars on this evolutionary pathway so close to our Milky Way galaxy presents us with an excellent opportunity learn even more about how these black hole binaries form.”
Co-author Daniel Pauli, a PhD student at the University of Potsdam, said: “This binary star is the most massive contact binary observed so far. The smaller, brighter, hotter star, 32 times the mass of the Sun, is currently losing mass to its bigger companion, which has 55 times our Sun’s mass.”
The black holes that astronomers see merge today formed billions of years ago, when the universe had lower levels of iron and other heavier elements. The proportion of these heavy elements has increased as the universe has aged and this makes black hole mergers less likely. This is because stars with a higher proportion of heavier elements have stronger winds and they blow themselves apart sooner.
The well-studied Small Magellanic Cloud, about 210,000 light-years from Earth, has by a quirk of nature about a seventh of the iron and other heavy metal abundances of our own Milky Way galaxy. In this respect, it mimics conditions in the universe’s distant past. But unlike older, more distant galaxies, it is close enough for astronomers to measure the properties of individual and binary stars.
In their study, the researchers measured different bands of light coming from the binary star (spectroscopic analysis), using data obtained over multiple periods of time by instruments on NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope (HST) and the Multi Unit Spectroscopic Explorer (MUSE) on ESO’s Very Large Telescope in Chile, among other telescopes, in wavelengths ranging from ultraviolet to optical to near-infrared.
With this data, the team were able to calculate the radial velocity of the stars – that is, the movement they made towards or away from us – as well as their masses, brightness, temperature and orbits. They then matched these parameters with the best-fit evolutionary model.
Their spectroscopic analysis indicated that much of the outer envelope of the smaller star had been stripped away by its larger companion. They also observed the radius of both stars exceeded their Roche lobe – that is, the region around a star where material is gravitationally bound to that star – confirming that some of the smaller star’s material is overflowing and transferring to the companion star.
Talking through the future evolution of the stars, Rickard explained: “The smaller star will become a black hole first, in as little as 700,000 years, either through a spectacular explosion called a supernova or it may be so massive as to collapse into a black hole with no outward explosion.
“They will be uneasy neighbors for around three million years before the first black hole starts accreting mass from its companion, taking revenge on its companion.”
Pauli, who conducted the modeling work, added: “After only 200,000 years, an instant in astronomical terms, the companion star will collapse into a black hole as well. These two massive stars will continue to orbit each other, going round and round every few days for billions of years.
“Slowly they will lose this orbital energy through the emission of gravitational waves until they orbit each other every few seconds, finally merging together in 18 billion years with a huge release of energy through gravitational waves.”
Reference: “A low-metallicity massive contact binary undergoing slow Case A mass transfer: A detailed spectroscopic and orbital analysis of SSN 7 in NGC 346 in the SMC” by M. J. Rickard and D. Pauli, Accepted, Astronomy & Astrophysics.
DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/202346055

“음악 팬. 매우 겸손한 탐험가. 분석가. 여행 괴짜. 익스트림 TV 전문가. 게이머.”